“On-Page SEO” concerns the first category, i.e. criteria specific to your site. Here we look at how to optimize these internal criteria to improve your referencing.
1. Navigation (or your website’s architecture)
A well-designed navigation offers two advantages: it allows visitors to quickly find whatever it is they are looking for, and search engines to efficiently browse the site by following the structure of the links.
A restaurant website will usually include generic categories such as the menu or business hours. Rather than trying to be inventive, you should give preference to a classic structure to simplify user browsing and allow search engines to optimally analyse your content. A good rule of thumb: it should be possible to quickly find all the information contained in your website, failing which, visitors are likely to quickly look elsewhere.
Here are the best practices to adopt to optimize your navigation.
Structure your website
A website should contain:
- a homepage
- your menu
- the business days/hours
- the address and location with a Google Maps link
Keep it simple. Visitors want to immediately find what they are looking for.
Choose your domain name wisely
Your domain name should be simple, easy to spell and contain the name of your company. Sometimes, your corporate name alone will not distinguish you from establishments similar to yours (such as “pizzeria”). In this case, use a term relating to your location (such as the town or region), or any other nearby noteworthy geographic point.
Optimize your site’s pages by keyword
To help Google effectively index your content, choose a keyword or a string of keywords for each page. Sample string of keywords: “pizza restaurant Manchester”.
Once you have decided on your keywords:
- place the keyword(s) in the title of the page
- remember to integrate the keyword’s semantic field (e.g. pizza / pizzeria)
- place the keyword(s) in the page’s URL (this is called “url rewriting”).
For example: www.pizzamanchester.com/pizza-delivery-manchester rather than www.pizzamanchester.com/p65841
The following should be avoided at all costs:
- Using high-traffic keywords that have nothing to do with your target’s expectations (e.g. such as the “Apple” brand). Risk: misleading internet users and seeing your bounce rate (the percentage of visitors to your site who navigate away from it after viewing only one page) go through the roof.
- Hiding keywords on your pages in white text against a white background, visible only by search engines. Risk: being penalized by Google, now able to detect such devious techniques.
Help the search engines to index your images
Robots/crawlers can’t read images. However, you can help them do just that by describing their content via keywords, placed in the “alt” tag of the image’s HTML code. For example: 
<img src=“photo-pizza.jpg” alt=“Pizza Manchester” / here, “img src=”….”.jpg” designates the photo’s location. The “alt” tag is used to add the photo’s description.
Optimize your logo
The logo is one of the very first elements identified by Web crawlers.
- Use strategic keywords to name your image. Thus, for example, it is better to use “pizza-delivery-manchester-logo.jpg” than “logo.png”.
- Add the ALT text to your logo: information concerning your activity, your location, your speciality… In the above example, you could specify “Pizza Delivery Manchester” in the ALT tag.
Optimize your page titles
Whether for the titles of your pages or those of your articles, it is important to insert strategic keywords in your titles since these attract the visitor’s attention. The more closely a page’s title matches whatever the visitor is looking for, the more the page is likely to feature among the leading results displayed. Here we talk of a page being “well ranked”.
Here are some rules to observe:
- A title should be unique for each page and each article
- A title should not exceed 55 characters
- A title should not be a sentence
- Use keywords at the beginning of the title
Optimize your homepage
A simple “Welcome” is not enough. Mention important information such as:
- The name of your restaurant
- Your location
- A concise, straightforward description of what your offer via strategic keywords
Enter the meta description of each page
In HTML, you can specify one meta description for each page on your site. This will be displayed in the search results, under the title of your page. Use this meta description to explain – in a few words – your activity or the page’s content. When reading this description, the visitor will decide on the importance of your site. Consequently, you should compose it carefully. The ideal length is 200 characters, including spaces. It should comprise one to two sentences containing a subject, a verb and an object. Insert keywords in this meta description.
For example :
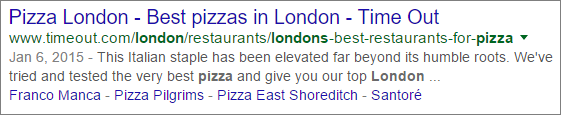
Each meta description must be unique to avoid any internal duplicate content.
Use keyword synonyms
Google is capable of going beyond the exact terms of a search to detect the intention of that search. That’s why, when referencing, you can use keywords and synonyms.
For example, the following synonyms may be associated with the “restaurant” keyword: canteen, inn, cafeteria, grill, etc. A search on the terms “Spanish cuisine in Leeds” will generate results directly relating to the expression, as well as an interesting result: “La Tasca Spanish Tapas Bar”. Here, the word “tapas” is associated with “Spanish” + “cuisine”. Google has understood our search intention, and is able to consider that these “tapas” correspond to our search.
Create content that’s unique
Google detects and penalizes content that is merely copied & pasted. Your content should thus be original and unique.
Keep an eye on your bounce rate
Google takes your bounce rate into consideration. If visitors quit your site without really looking at it, its positioning will be penalized accordingly.
One way to reduce the bounce rate is to use images and video. By attracting the visitor’s eye, you will encourage them to continue looking. You will also increase your chances of acquiring a new customer.
What is a good bounce rate? That depends on the business sector, the nature of the site (e-commerce site, blog, information site, etc.) and the level of competition for the keywords targeted. A bounce rate below 40% is a good target. To measure and control this rate, you can install Google Analytics on your site.
Optimize your website’s load speed
A site that takes too long to load will deter most internet users. There are a number of free tools available to measure your site’s load speed:
Create internal links containing plenty of keywords
Internal links connect your pages up to one another. A link’s “anchor” is the word or phrase on which a visitor clicks to access that link. Google takes this link into consideration in its target page referencing. Give preference to descriptive anchors, such as “our business hours”, over generic anchors such as “Find out more”.
Check your links
Make sure to regularly check that your links are working. A “404 Not Found” error (broken link) will no doubt scare away your visitors, to say nothing of search engines.
2. Write a blog
Not so long ago, lots of companies created blogs for the sole purpose of improving their referencing. Crammed full of keywords, these blogs were never promoted since they were not intended for real readers. Those days are over. Today, a blog can represent a veritable communication tool.
Having a blog means you can:
- Strengthen your brand’s identity
- Announce news
- Position yourself as an expert
- Attract visitors via interesting content before transforming them into customers
- Show what goes on “behind the scenes”
The restaurant industry lends itself very well to this method of communication. Don’t pass up on this precious tool; not only can it enhance your image, it will also ensure that the search engines find you!
3. Enhanced data
Tag tools are used to tag your website’s content, i.e. to point out the meaning of your content to Google. If Google correctly interprets the content of your pages, it will be able to create “rich snippets”. Rich snippets represent all the detailed information that will allow internet users to know whether your site matches their search. These rich snippets can help you improve your pages’ click rate and thus increase your traffic (consequently, in the long run, they have a positive impact on your referencing). Rich snippets for restaurants can include, for example:
- opinions
- a price range
- an average rating, and so on.
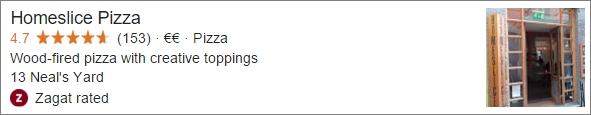
Go here to add tags. Fill in all the requested elements by clicking on your pages: name, telephone, address, business hours, etc.
Conclusion On-Page SEO is a key step for improving your referencing. However, Off-Page SEO, which concerns links external to your website, is a complementary device that must also be considered. Once combined, these two methods will give you every chance of improving your referencing. We will discuss Off-page SEO in a future article.